Spinal Arthritis: Early Signs And What To Do About It
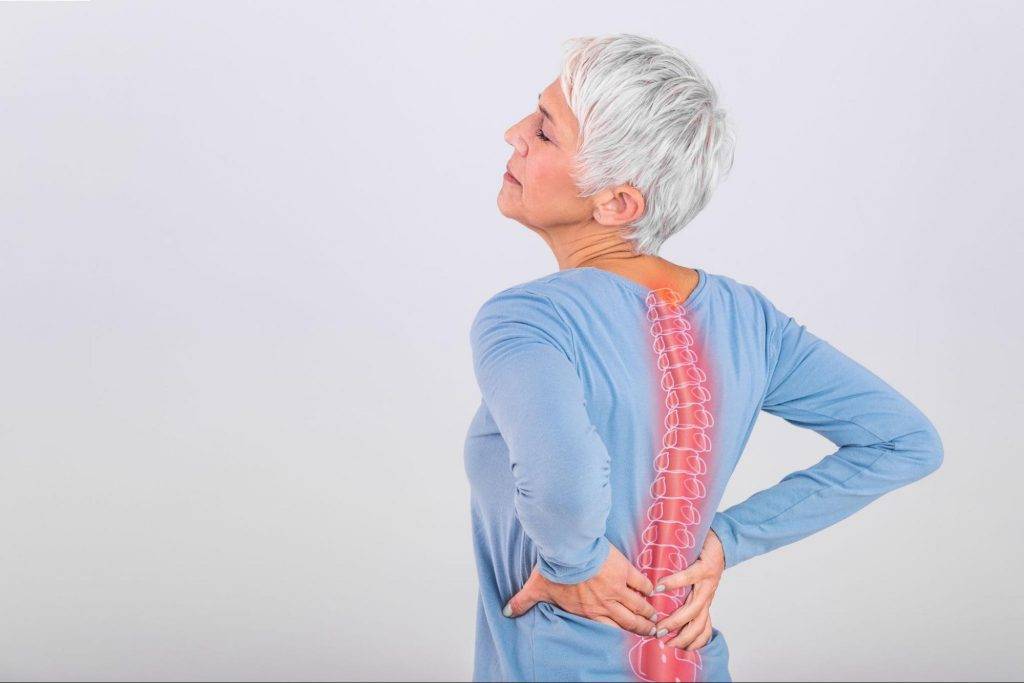
Even though it is a common cause of back pain, many people rarely suspect arthritis.
Usually, mild back pain will go away on its own within a few days or weeks. However, if your pain is due to a chronic condition such as arthritis, the pain will persist. Back pain from arthritis can be debilitating, but it doesn’t have to be. Proper diagnosis and treatment of your symptoms can relieve your pain and improve your mobility.
Read on to learn more about the symptoms of spinal arthritis, common forms, and your treatment options.
Spinal Arthritis
An estimated 30.8 million US adults have osteoarthritis, the most common form of spinal arthritis. It is the fifth most common disease worldwide.
What It Is
Inflammation in the facet joints in the spine or the sacroiliac joints between the spine and pelvis results in spinal arthritis. Arthritis of the back may be due to wear and tear, autoimmune disorders, infection, and more. Spinal arthritis in the neck or back can be painful and may become chronic.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of spine arthritis are low back pain and stiffness. The symptoms are usually worse in the morning, presumably because fluid builds up due to inactivity overnight. As you are more active during the day, the symptoms tend to ease but may worsen again in the evenings.
Flare-ups of symptoms are also common during the winter months.
Additional symptoms of spinal arthritis include:
- Back and/or neck pain
- Pain that disrupts sleep
- Swelling or warmth in the joints
- Localized tenderness
- Loss of flexibility or range of motion in the affected joint or area
- A feeling of pinching, tingling, or numbness
Types Of Back Arthritis
There are many types of arthritis. When it comes to the back, they fall into two categories, mechanical and inflammatory. Mechanical back pain includes osteoarthritis and is more common. Inflammatory back pain includes forms of rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis.
Inflammatory and mechanical forms of arthritis are treated differently so it is important to be properly diagnosed first.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the spine is a degenerative joint disease and the risk increases with age. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage cushioning the bones or joints wears down over time.
In addition to affecting the spine, osteoarthritis is commonly found in the hips, hands, and knees. The symptoms can be managed and the progression of the disease may be slowed, but not reversed, with treatment.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is actually an autoimmune disease that causes joint pain and damage throughout the body. This chronic disease has flare-ups and periods of remission. As a form of inflammatory arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis causes pain and inflammation in the joints. While it typically affects the limbs, it can also impact the spine.
Spondyloarthritis
Spondyloarthritis is an umbrella term for different types of arthritis that namely cause inflammation in the spine. This form of arthritis involves inflammation where the ligaments and tendons attach to the bone. Forms of spinal arthritis within this category include:
- Axial spondyloarthritis – Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis involves inflammation in the spine but joint damage is not visible on x-rays. Ankylosing spondylitis involves bony growths on the spine.
- Reactive arthritis – This form of arthritis is in response to an infection or illness in the body. Reactive arthritis may be caused by gastrointestinal illnesses, STDs, or urinary tract infections.
- Psoriatic arthritis – Although this often affects the fingers, toes, and knees, up to half of psoriatic arthritis patients have spine inflammation.
Diagnosing Spine Arthritis
Diagnosing arthritis of the back requires a comprehensive evaluation and review of your medical history. You will need to recall your symptoms, when they started, and how they have changed.
Your physician will complete an exam to check your overall health, musculoskeletal status, nerve function, reflexes, and problematic joints. Medical tests may be requested to check for joint damage, compression fractures, bone spurs, and cartilage loss.
How Spinal Arthritis Is Treated
Back pain from arthritis affects your everyday life. Thankfully, lifestyle changes and treatments can help improve your quality of life.
Treatment Options
The goal of spinal arthritis treatment is to ease pain and increase functionality. Your physician will help you lead a healthy lifestyle to improve your symptoms. Treatments may include:
- Weight management
- Exercise
- Rest
- Hot and cold compresses
- Massage
- Nutritional supplements
- Pain medication
- Corticosteroid injections
- Stem cell therapy
Best Exercises for Spinal Arthritis
Exercise and self-care activities are safe for most patients with arthritis of the neck and back. However, it is always a good idea to consult your physician before starting a new exercise regimen.
It is important to stretch and strengthen your back. This keeps the muscles that support your neck and spine strong and flexible. Exercises for spinal arthritis may include:
- Neck and back exercises to build strength.
- Low impact aerobic exercises to control your weight and keep your heart and lungs in shape.
- Range of motion exercises to relieve stiffness and keep the joints limber.
Contact Advanced Sports & Spine
Arthritis of the back can be treated to ease your pain and improve your range of motion. At Advanced Sports and Spine, we provide spinal arthritis treatment in Charlotte. Dr. Ahmad utilizes an integrative approach to pain management and uses the latest techniques and technologies.
Stop living with chronic pain! Book an appointment with Advanced Sports and Spine today.